陽明交大資工所碩一上(2023 Fall)修課心得
作業系統
- 英文課名:Operating System
- 永久課號:CSIC30015
- 教師:吳俊峯
課程內容
因為沒上過交大這邊教的大學部 OS,所以不知道跟大學的差別有多少。但是體感上跟清大差不少。清大周志遠教授的 OS 感覺比較想是每個 component 都碰一下,但是這堂比較偏向每個都會教到比較深層的。但可能時間的關係,所以也沒有辦法教很多很深。老師好像是作記憶體的(他下學期還有開一門〈記憶體與儲存系統〉),所以那段講的特別細節和清楚。
因為沒上過交大這邊教的大學部 OS,所以不知道跟大學的差別有多少。但是體感上跟清大差不少。清大周志遠教授的 OS 感覺比較想是每個 component 都碰一下,但是這堂比較偏向每個都會教到比較深層的。但可能時間的關係,所以也沒有辦法教很多很深。老師好像是作記憶體的(他下學期還有開一門〈記憶體與儲存系統〉),所以那段講的特別細節和清楚。
從郵局匯款到 Fristrade,綁定約定到入帳最快可能可以四天完成。兩天是綁定的時間,兩天是匯款的時間。郵局這邊的手續費因為活動期間,用行動郵局 App 轉帳只要 168。之後最便宜應該也要 300 + 100。中轉行收 15 USD。
由磁盤組成,最小儲存單位是 sector,買來就切死的,所以用軟體的 block (多個 sector)來控制。Sector 會有 number,所以可以對特定資料作讀取。
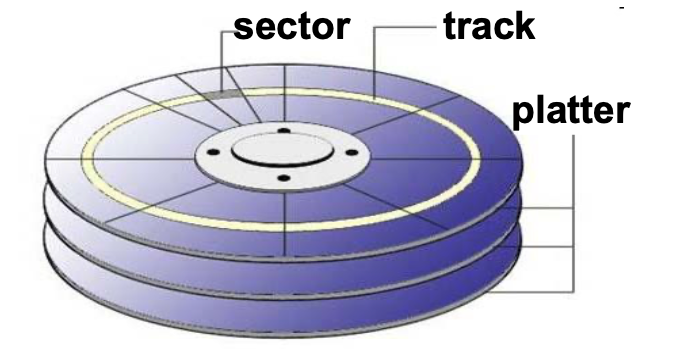
Density of bits per track 是固定的
這樣內圈的資料量就會小於外圈的
但是這樣讀取資料的速度會不固定
→ 讀內圈要轉比較快
applications: CD-ROM and DVD-ROM
電腦不是在做 I/O 就是在做計算
I/O devices: tape, HD, mouse, joystick, network card, screen, flash disks, etc
I/O subsystem: the methods to control all I/O devices
Two conflicting trends
Device drivers: a uniform device-access interface to the I/O subsystem
⇒ Similar to system calls between apps and OS
Device categories
Port: A connection point between I/O devices and the host. 每個 port 都有自己的 ID,那就是 device 對於電腦的 identifier。
→ E.g.: USB ports
Controller: A collection of electronics that can operate a port, a bus, or a device
⇒ A controller could have its own processor, memory, etc. (E.g.: SCSI controller)
Bus: A set of wires and a well-defined protocol that specifies messages sent over the wires(連接的方式,除了物理相接,還有 protocol 的部分)
→ E.g.: PCI bus
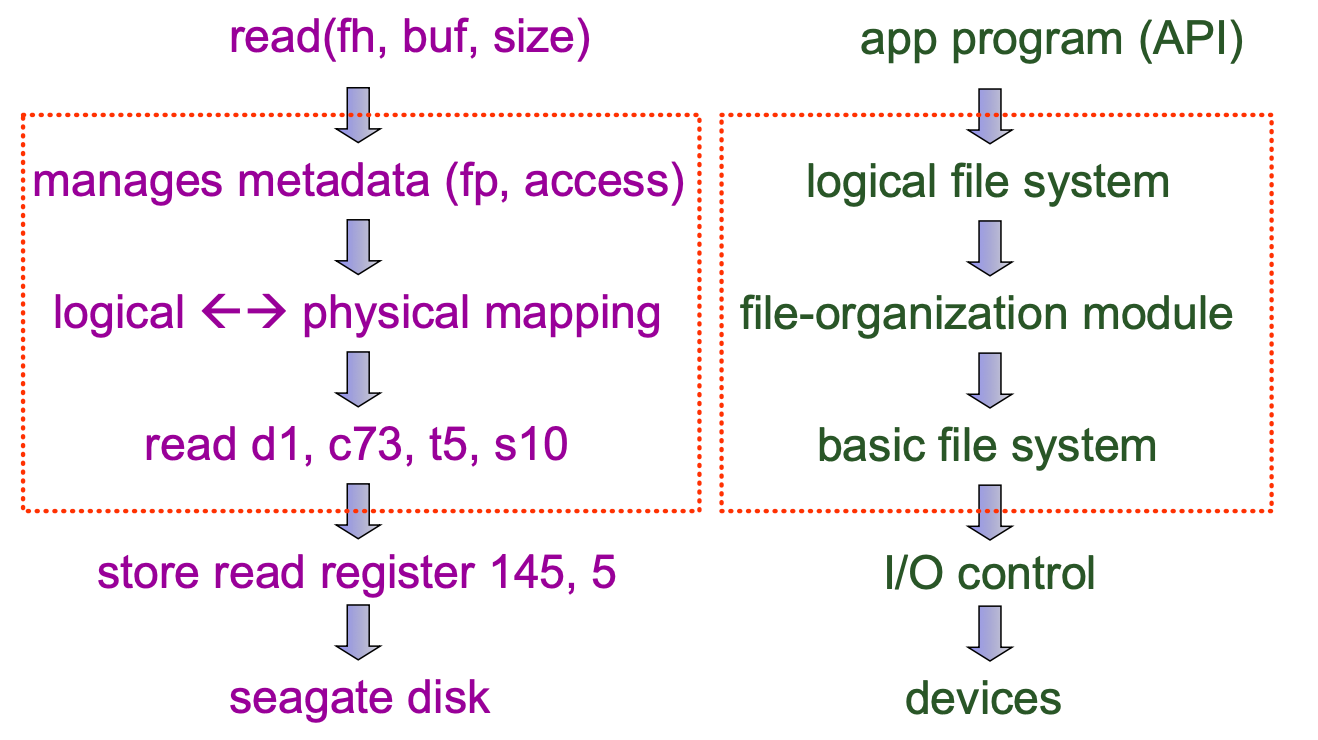
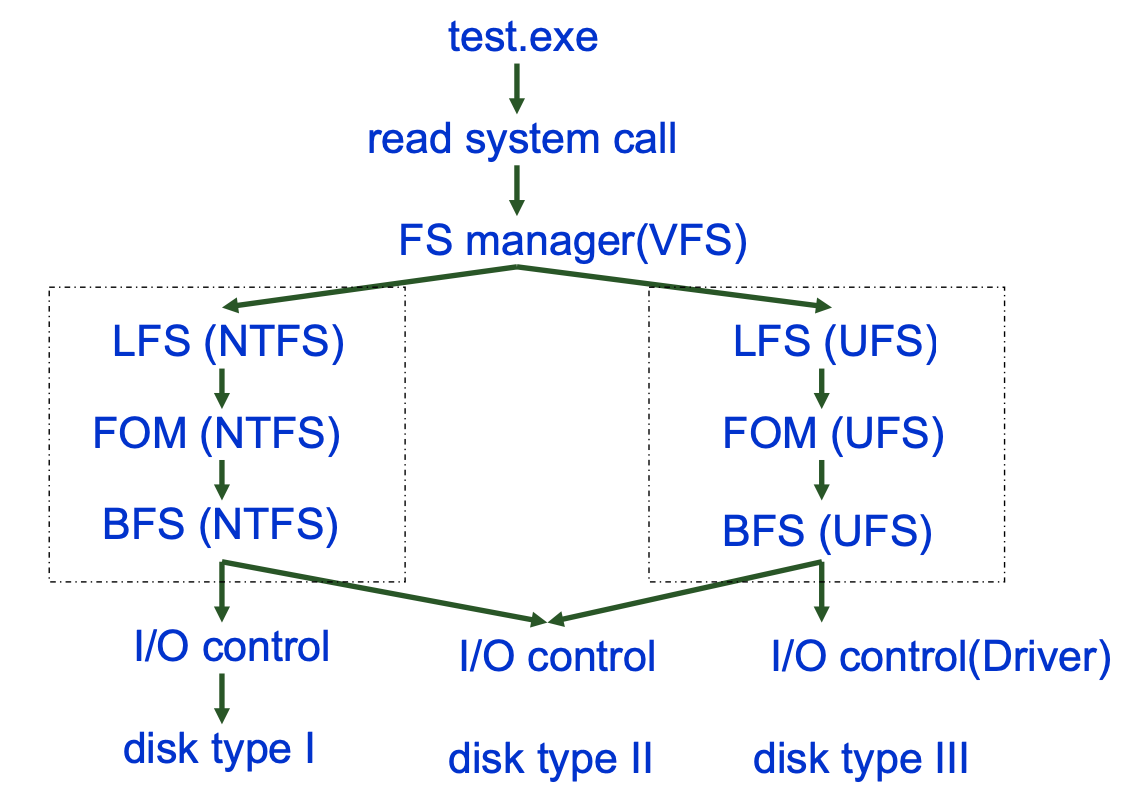
之所以一個 fread 可以對不同的 file system
作操作就是中間有 FS manager (VFS — Virtual File System)
File 也是抽像的概念。
Physical storage unit in disk

File attributes (Metadata)
File operations
Necessary Condition → 一定要全部的條件同時發生
Mutual exclusion — 資源是沒有共享性的(暫時)
Hold and Wait — 會 hold resource 然後 wait 別人
No preemptive — 不能強制別人放開 resource
Circular wait — 一定會有一個 circular 的 wait。
\(P_0 \rightarrow P_1 \rightarrow P_1 \rightarrow \dots\rightarrow P_n \rightarrow P_0\)

用 counter 去記還有幾個空位
Producer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7while (1) {
nextItem = getItem( );
while (counter == BUFFER_SIZE);
buffer[in] = nextItem;
in = (in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
counter++;
}
Consumer
1
2
3
4
5
6while (1) {
while (counter == 0) ;
item = buffer[out];
out = (out + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
counter--;
}
但是 counter 會是這兩隻 thread 共用的東東,所以會出現不一致的問題:
counter++
1
2
3move ax, counter
add ax, 1
move counter, ax
counter--
1
2
3move bx, counter
sub bx, 1
move counter, bx
但是…如果是這樣呢?(counter initially is 5)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9producer: move ax, counter // ax = 5
producer: add ax, 1 // ax = 6
context switch
consumer: move bx, counter // bx = 5
consumer: sub bx, 1 // bx = 4
context switch
producer: move counter, ax // counter = 6
context switch
consumer: move counter, bx // counter = 4
不過如果不是 preemptive 就不會有這個問題了。
因為 multiprogramming 所以才要 scheduling。
→ 東西要嘛在 CPU 要嘛在 I/O

所以每一個 process 就切成在 CPU burst 和在 I/O burst
I/O-bound program → 大部分在做 I/O
⇒ 不等於 I/O burst 的 cycle 數比 CPU 多(數量應該要是一樣的,因為一個做完接另一個),應該要是一個 burst 要很久。
CPU-bound program → 大部分在做 CPU
CPU 大多是短的 burst 很多

Ready state → Running state
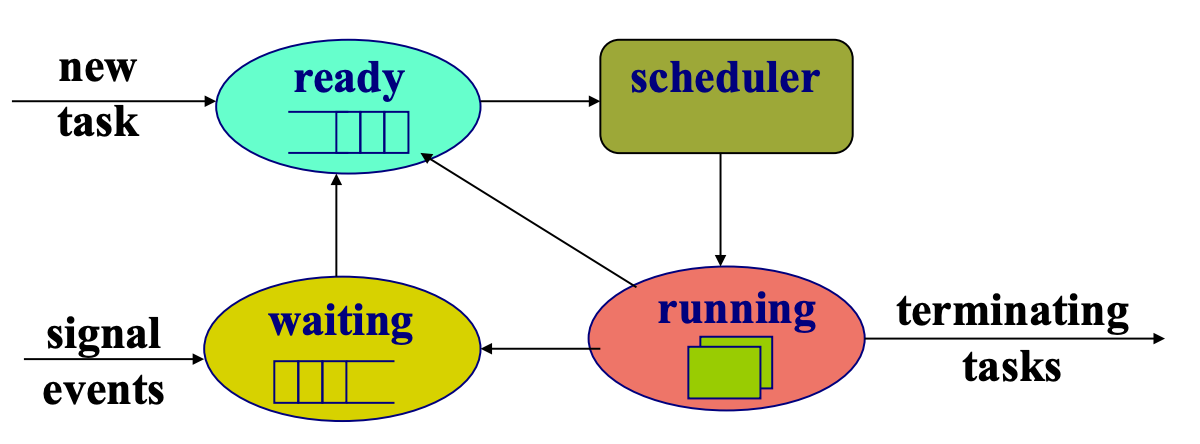
下面都假設是 single core,只有單一隻程式
網路溝通可以分成兩種主要的 API
HTTP/2: the difference between HTTP/1.1, benefits and how to use it
→ 幫 HTTP 套規則